Health Benefits and Uses of Cannabidiol (CBD) – Plus Side Effects to Know
The cannabis plant contains over 200 naturally occurring chemical compounds known as cannabinoids. Among them, the most prominent are cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). While THC is widely known for its psychoactive effects, CBD is non-intoxicating and increasingly recognized for its potential health benefits.
Cannabis is primarily categorized into two species: Cannabis indica and Cannabis sativa. Both contain CBD and THC, but only Cannabis sativa can be cultivated to produce industrial hemp—a renewable, biodegradable crop used in the production of textiles, biofuels, building materials, and paper.
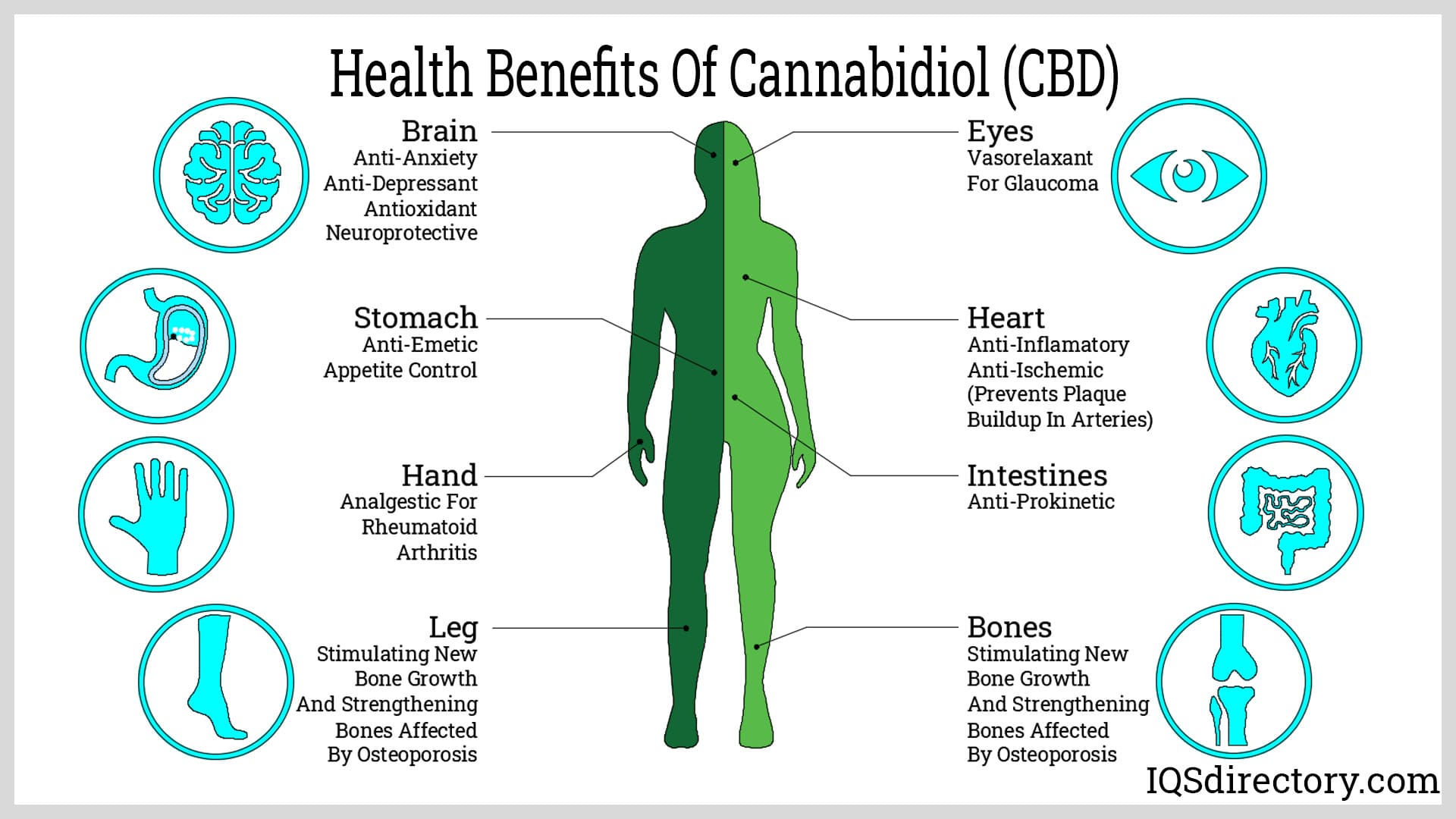
What is Cannabidiol (CBD)?
The psychoactive nature of THC has often led to confusion around CBD. Unlike THC, CBD is non-psychotropic, meaning it does not produce a high and has no addictive or habit-forming qualities. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there is no evidence of public health issues related to the use of pure CBD.
Despite regulatory barriers historically limiting research, CBD is widely studied for its potential to alleviate various health conditions. Both CBD and THC are extracted from Cannabis sativa or hemp plants and are federally legal in the United States as long as the THC content does not exceed 0.3%.
Health Benefits and Side Effects of Cannabidiol (CBD)
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurring seizures, affecting over 60 million people worldwide. In 2018, clinical trials showed that CBD significantly reduced seizure frequency in patients with Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. In response, the FDA approved Epidiolex, a CBD-based medication for children as young as two years old, later expanding its use to treat tuberous sclerosis complex in patients aged one and older.
However, CBD may interact with other antiepileptic medications like valproate, potentially impairing liver function.
CBD affects epilepsy by binding to the brain receptors found in the endocannabinoid system (ECS) of the brain. In the same year as the CBD epilepsy study, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Epidiolex, a seizure control medication made from CBD, as a treatment for severe forms of child onset epilepsy for patients that are two or older. In 2020, the FDA expanded the use of Epidiolex to treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex and lowered the age of legal usage to one.
Cannabidiol can interact negatively with other epilepsy medications and cause serious and severe side effects such as a decrease in liver function when given to patients taking valproate.
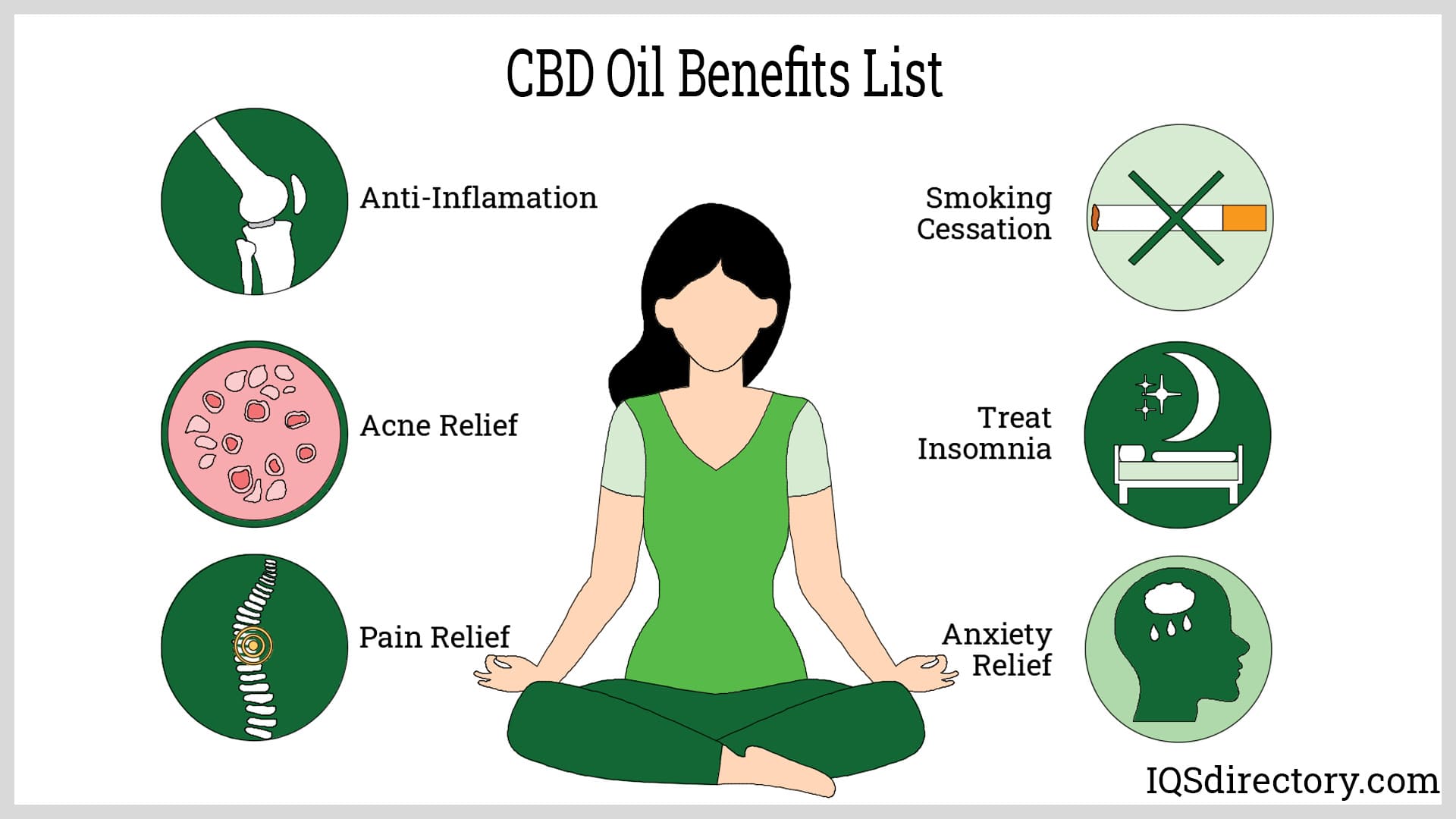
Pain Relief
Cannabis oil has a long history of use in managing pain. CBD works by interacting with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates functions such as pain perception, immune response, and inflammation. Animal studies show that CBD reduces pain and inflammation by influencing ECS receptors and enhancing serotonin levels.
Although human research is still developing, Health Canada has approved a THC-CBD combination spray for pain relief in multiple sclerosis and cancer patients. However, CBD may negatively interact with medications used for heart disease and immune suppression, making it unsuitable for those individuals without medical supervision.

In several studies on animals, CBD was found to have anti-inflammatory effects and worked on the pain sensing aspects of the endocannabinoid system. There have been very few studies on humans, but Health Canada has approved the use of a combination of CBD and THC to relieve central nervous system related pain from multiple sclerosis and cancer, diseases that are unresponsive to opioid treatments.
In the animal studies, it was found that CBD has an effect on serotonin levels. Low levels of serotonin play a major part in mood and pain. The anti-inflammatory effects of CBD have also been found to have an effect on pain.
CBD interacts negatively with medications for treatment of heart conditions or immunosuppressants and is not recommended for treatment of pain for those diseases. Though it is believed that CBD is good for relieving pain, there are no human studies that conclusively prove this to be true.
Arthritis
More than 54 million Americans suffer from arthritis, a condition that causes joint pain and inflammation. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder affecting hands and feet, while osteoarthritis deteriorates cartilage in weight-bearing joints like hips and knees.
Animal studies conducted between 2006 and 2018 suggest that CBD may relieve arthritis-related pain and inflammation. While human clinical evidence remains limited, anecdotal reports are promising. For arthritis, topical CBD creams are preferred, as oral ingestion may lead to digestive discomfort and reduced efficacy.
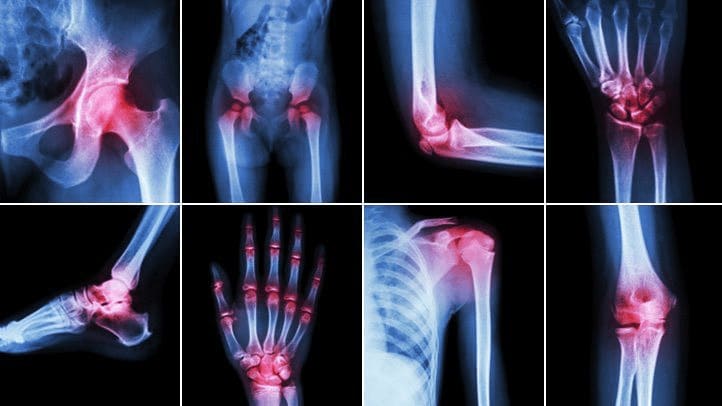
CBD is best applied as a topical cream for arthritis, as ingesting it may lead to gastrointestinal issues and reduced absorption.
Some of the studies used both CBD and THC as a spray. Though the present studies are encouraging, there is no conclusive evidence that CBD is a possible treatment for arthritic pain.
If CBD is used for arthritic pain, it should be used topically since ingesting it has negative effects and may lead to gastrointestinal complications. Also, if CBD is taken orally, it is not absorbed by the body.
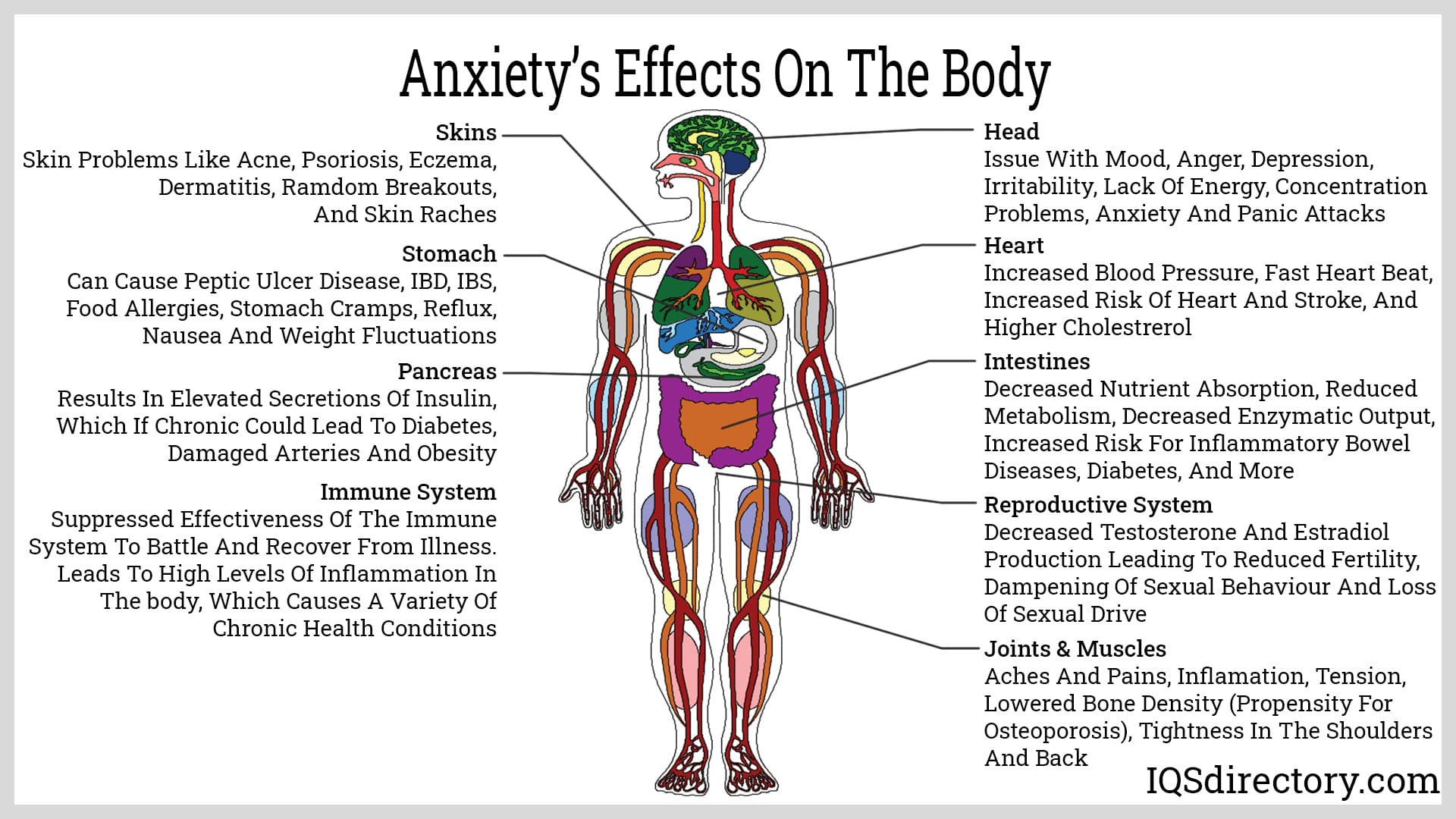
Anxiety
Anxiety is a natural response to stress, but for many, it becomes chronic and debilitating. Disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), PTSD, social anxiety, panic disorder, and phobias. Contributing factors may include trauma, genetics, health conditions, or stimulant overuse.
Clinical trials administering between 150 mg and 600 mg of CBD found that nearly 80% of participants experienced a decrease in anxiety levels. Most subjects were tested in high-stress scenarios such as public speaking, suggesting CBD may be especially helpful for social anxiety and performance-related stress.
There have been several human studies related to the use of CBD to relieve anxiety. Each study group was given differing levels of CBD from 150 mg up to 600 mg. A significant study found that nearly 80% of the subjects had a decreased anxiety score on the testing instrument after taking doses of CBD.
Each of the test groups were given doses prior to speaking events that normally made them anxious. The only conclusion that can be drawn from the results is that CBD is a beneficial method for preventing anxiety for public figures and those who participate in public speaking and presentations.
Depression
CBD may serve as a natural alternative to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for depression. It appears to increase serotonin availability in the brain, leading to improved mood regulation.
Animal studies support these findings, although more human research is needed. Potential side effects include fatigue, dry mouth, nausea, and interactions with other medications. CBD should be avoided by children, pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, and those taking certain prescription drugs.
The most common method for treating chronic depression is serotonergic (SSRI) medications that lead to weight gain, insomnia, and sexual dysfunction. Though SSRI has proven to be a successful treatment, it does lose its effectiveness if used over a long period of time. The solution to the problems with SSRI has been the discovery and use of CBD.
CBD oil works in the same way SSRI does and blocks the production of serotonin, forcing the serotonin to be used in the synaptic space. When serotonin is properly used by the brain, people experience more stable and contented moods free of stress and depression. CBD can be taken as an oil or be used in a vape pen.
The most recent studies on the use of CBD as a means to fight depression have been completed on animals. The research measured the effects of CBD on serotonin levels with positive results. The reported side effects of using CBD for depression are fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, dry mouth, and low blood pressure. Certain people should avoid the use of CBD for depression; these people include children, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and anyone taking another potentially incompatible medication.

Acne
CBD’s anti-inflammatory and oil-reducing properties may benefit those with acne. It has been shown to inhibit sebum production and calm inflammation in sebaceous glands.
In a 12-week study, participants applying CBD twice daily noted visible improvements in acne scars and overall skin condition. Reported side effects include dry mouth, fatigue, and changes in appetite.
There have been positive results regarding the use of CBD in dealing with acne scars caused by enlarged eruptions and damage to the skin by picking at the eruptions. In a study, participants applied CBD twice a day for three months and had significant improvement in the appearance of their skin.
The side effects of CBD for acne treatment are loss of appetite, dry mouth, fatigue, and diarrhea. Some people believe that CBD is useful for the treatment of acne rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, eczema, and dermatitis.
High Blood Pressure
CBD may help lower blood pressure by dilating blood vessels and reducing stress. A 2017 UK study found that a single dose of CBD significantly reduced blood pressure in test subjects under stress.
However, side effects may include cold extremities, dizziness, and potential interference with medications. As with other conditions, proper dosage should consider individual physiology.
While CBD is effective in treating hypertension, the potential side effects can be cold feet and hands, insomnia, dizziness, and depression as well as symptoms that are similar to asthma such as irregular heartbeat and erectile dysfunction. It is essential that it is not taken in conjunction with other medications.
CBD can be taken for heart conditions in a variety of forms, including as edibles, drops, capsules, and vapes. The dosage of CBD has to be coordinated with the physical characteristics of the patient such as weight, height, genetics, and metabolism.

Psoriasis
Psoriasis causes painful, scaly patches on the skin due to excessive skin cell buildup. CBD may help regulate skin cell turnover, reduce inflammation, and support the immune response.
Though promising results have come from cell and animal studies, human trials are still limited. Side effects are generally mild but may include dry mouth and drowsiness.
Several recent studies, one in 2007 and one in 2019, have shown very promising results regarding the benefits of using CBD for psoriasis. The American Academy of Dermatology has stated that CBD has anti-inflammatory properties that have been proven to be effective against a variety of skin disorders.
The collected data from the many studies indicate that CBD has low toxicity when used for psoriasis treatment, with the possible side effects of sleepiness, dry mouth, and nausea. One study stated that high or uncontrolled doses of CBD can lead to liver damage, but the results have not been replicated.
Sleep Disorders
CBD is commonly used to aid sleep by reducing anxiety and chronic pain—two leading causes of insomnia. Some research suggests it may influence sleep-wake cycles via ECS receptors.
However, results are mixed, and optimal dosage and timing remain unclear. Reported side effects include fatigue, digestive changes, and reduced appetite.
Much of the research is unclear as to the positive effects of CBD for sleep. Some subjects reported very positive results and view CBD as a cure to their sleep problems. Other people experienced no change in their sleep habits. The final conclusion is that CBD can help calm negative thoughts that interfere with normal sleep patterns.
The effectiveness of CBD in treating sleep problems is unclear and is still being studied. There are potential side effects, which include fatigue, diarrhea, changes in weight, and loss of appetite.

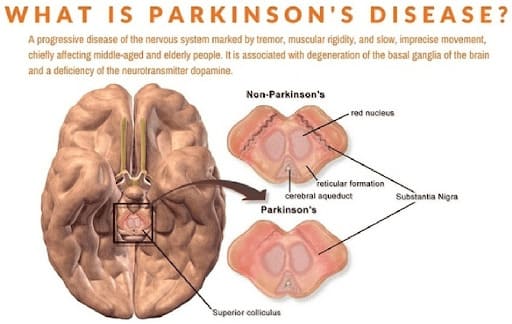
Parkinson‘s Disease
CBD may offer relief from Parkinson’s-related symptoms like tremors, insomnia, and psychosis. It has shown neuroprotective and antipsychotic effects in animal studies and early clinical trials.
While research is ongoing, CBD appears to be a safer alternative to THC-based treatments for managing Parkinson’s symptoms.
Though there have been studies regarding the use of THC as a method of suppressing Parkinson‘s symptoms, THC has been found to have several drawbacks and negative effects. A wider spectrum of data is available regarding CBD, which continues to be studied as a means for alleviating Parkinson‘s symptoms. CBD is a safer method with limited side effects.
Nausea and Vomiting
CBD interacts with serotonin receptors to reduce nausea and vomiting, especially in chemotherapy patients. It modifies serotonin receptor activity, easing discomfort caused by emetic agents.
There are two types of chemoreceptors: Dopamine D2 and Serotonin 5-HT3. CBD oil interferes with the feelings of nausea by interacting with the receptor 5HT3A that loosens the receptors bound to the serotonin and dopamine receptors and lessens the feelings of nausea and vomiting.
There are several reasons for people becoming nauseous, including anxiety, stress, pain, digestive issues, head injuries, and the arteries of the lower brain. The receptors that control nausea are located in the lower brain. There has been positive evidence from animal studies that CBD can help in regulating nausea and vomiting.
Cancer
Though not a cure, CBD may support cancer patients by reducing pain, nausea, and inflammation related to treatments. Research into its anti-tumor effects is ongoing but remains inconclusive.
CBD may interact with chemotherapy drugs and affect liver function. Product purity and labeling accuracy remain concerns due to lack of regulation.
The biggest concern for CBD oil as a way to treat side effects of cancer treatment is the fact that it is unregulated since it is marketed as a supplement. With a lack of restrictions, it is difficult to know how much CBD is in a product with certain products having less CBD and more THC. Further concerns are production methods that can produce possible contamination and impurities.
There are several side effects associated with the use of CBD in cancer treatment. The most prominent of the concerns is the damage to liver function. It has also been found that CBD inhibits enzymes responsible for metabolizing certain drugs, which can affect how drugs work and affect the body. At the top of the list of treatments affected by CBD is chemotherapy, which can become dangerous when combined with CBD.
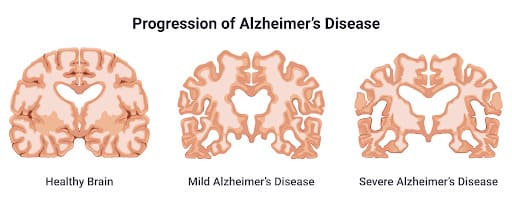
Alzheimer‘s
CBD may provide neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant benefits that support cognitive function. It may also promote neurogenesis, potentially slowing Alzheimer's progression.
Animal research shows potential, but more human studies are needed. Possible side effects include bloating and liver enzyme alterations.
Since there is not a cure for Alzheimer‘s, the various treatments are focused on controlling and easing the symptoms of the disease. The most compelling evidence indicates that neuroinflammation contributes to its development. Specific genes related to immune receptors seem to be involved in its development.
Recent research indicates that CBD promotes the production of neurons, the cells that are lost during the onset of Alzheimer‘s. Animal studies have shown that CBD reverses and prevents cognitive dysfunction. Additional results have indicated that the combination of CBD and THC can be used as a treatment since CBD inhibits the psychoactive effects of THC.
As with other treatments using CBD, there are serious side effects related to the interaction of CBD with other drugs. The most common potential side effects are diarrhea and bloating with a few users experiencing liver problems.
Diabetes
In preclinical trials, CBD reduced blood glucose, improved insulin production, and decreased blood flow complications in diabetic animals. However, no conclusive human studies confirm these findings.
Potential side effects include dry mouth, drowsiness, and diarrhea. Label inconsistencies are common, so sourcing from reputable producers is essential.
The studies and experiments regarding CBD as a method for controlling or curing diabetes have been conducted on mice and rats. In one study, it was found that CBD decreased the flow of blood to the brain, reversing a complication created by diabetes. Further results indicated that CBD cut down on high blood sugar, lowered cholesterol, and increased insulin production.
The side effects of using CBD for diabetes include fatigue, drowsiness, diarrhea, and dry mouth. Since CBD products are unregulated, their labels may have misinformation and neglect the inclusion of details regarding other chemicals that may be present in the product.
Schizophrenia
CBD may help manage psychosis symptoms and act as a neuroprotective compound. It influences the ECS and immune system to reduce inflammation and protect against memory loss.
Studies suggest CBD may be as effective as traditional antipsychotic drugs without the same side effects. Delivery methods include oral, inhaled, or intravenous administration.
Though there is no cure for schizophrenia, there are methods available to cure and control psychotic episodes. The endocannabinoid and endogenous cannabinoid systems are involved in the neuropathology of a psychosis such as schizophrenia. CBD is a type of therapeutic agent since it indirectly affects the endocannabinoid system.
Several studies have shown that CBD has neuroprotective properties due to its ability to prevent neuroinflammation and its impact on the immune response to neurological disorders. Other data has shown that CBD is a method for preventing memory impairment. The many animal studies suggest that CBD possesses the same characteristics as antipsychotic drugs.
For use as an antipsychotic, CBD can be taken orally, intravenously, or through inhalation without producing any side effects or toxicity. There is evidence derived from imaging, behavioral studies, animal models, epidemiological studies, and clinical studies that seem to indicate that CBD may have the same potency as other antipsychotic drugs.
Conclusions:
CBD continues to gain popularity as a natural option for managing various health conditions. While early research is promising, more high-quality human studies are needed to confirm its long-term safety and effectiveness.
As with any supplement, CBD should be used with caution—particularly when combined with other medications. Side effects may include digestive issues, changes in appetite, and rare liver complications. Always consult a healthcare professional before beginning CBD treatment.
With growing interest and ongoing studies, CBD holds exciting potential in the future of integrative health and wellness.
Though there is the possibility of negative factors regarding the use of CBD as a medicinal or medical treatment, there is still a large amount of information that we do not know about its use and its benefits. What is very clear is that CBD has been used for thousands of years to improve health and as a preventative measure. Modern research and scientific study is working diligently to find how society can benefit from its use.
