The Ultimate Guide to Cannabis Oils
Introduction
This in-depth guide explores cannabis oil, its many forms, extraction methods, and wide-ranging applications.
Whether you're new to the topic or looking to deepen your understanding, this article covers:
- What is cannabis oil?
- Common methods for extracting cannabis oil
- Types of cannabis oil and their key differences
- The most effective uses and health benefits
- And much more...

Chapter One : What is Cannabis Oil?

Cannabis oil is a plant-based extract derived from both hemp and marijuana—two types of cannabis plants categorized by their THC content. By legal standards, cannabis plants containing less than 0.3% tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are classified as hemp, while those exceeding that threshold are considered marijuana.
Hemp is primarily cultivated for its high levels of cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is federally legal across all 50 U.S. states. CBD is widely used in wellness supplements, skincare, and pharmaceuticals. However, the purity and potency of cannabis oil depend largely on the extraction method, which can vary significantly in terms of safety, efficiency, and yield.
Chapter Two : Processing Methods for Extracting Cannabis Oil
Cannabis oil extraction is a rapidly evolving field, offering multiple techniques for isolating beneficial cannabinoids like CBD and THC from the cannabis plant. These methods are crucial in determining the purity, potency, and safety of the final product. Extraction techniques fall into two broad categories: solvent-based and mechanical (solvent-free) methods.
Processing Methods for Extracting Cannabis Oil
Harvesting
The cannabis plant can be grown indoors and outdoors. Though both methods produce a viable product, it takes several weeks for the flowers to mature, with indoor plants taking eight weeks and outdoor plants taking even longer.
Every garden is different in regards to harvesting the cannabis plant. How the plant is harvested has a significant impact on the quality, effect, and durability of the finished product. Regardless of the differences in the types of gardens, there are certain basic procedures that are always followed during the harvesting process; these include removal of the leaves, trimming, and removal of the flowers, which are also referred to as buds.
-
Leaf Removal

Marijuana Leaf (from hoosiergardener.com)
In this case, the leaves to be removed are the large fan leaves in the typical pattern of marijuana leaves. They can be plucked, cut, or removed with a trimmer. The large leaves do not contain a significant amount of cannabinoids and are usually disposed of. Once the larger leaves are removed, the remaining leaves can be removed immediately using wet trimming or you can allow the plants to dry before trimming.
-
Drying
Drying can happen after the wet trim method or right after the leaves are removed. As can be seen in the image below, the plants are hung upside down in trimmed small bunches or the whole plant is hung upside down. The plants dry at 65° to 75° F with a humidity factor of 45 to 55%. The drying process is completed in total darkness since the sun, UV rays, and light damage the cannabinoids or terpenes in the flowers. It takes seven to ten days to complete the cycle.
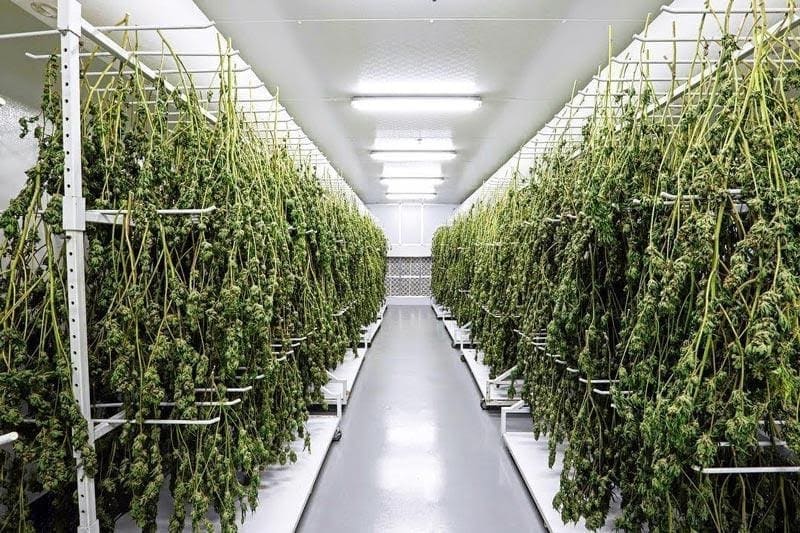

Cannabis Drying (from terpenesandtesting.com)
-
De-Stemming

Flower Removed from the Stalk (from growweedeasy.com)
The de-stemming process is removing the flowers from the central stalk. A cutting tool is used to sever the connection of the flower to the stalk by snipping it at the base of the flower. Though the process can be completed by hand, there are automated methods available.
-
Sorting

Automated Sorting Machine (from herb.co)
The sorting process is a simple matter of separating the different sizes of flowers and is completed to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the final trimming process.
-
Trimming Flowers

Cannabis Trimming Machine (from newswire.com)
The purpose of trimming the flowers is to remove the pieces of leaves that are stuck against the flowers. This exposes the flowers, which contain the greatest concentration of the cannabis chemical. Completing this process by hand is time consuming and requires extra labor. Using a trimming machine simplifies trimming and speeds it up.
-
Curing

Flowers Curing in Jars (from hightimes.com)
Curing is the final step in harvesting and is completed after the flowers have been satisfactorily trimmed. Curing is drying the flowers very, very slowly; this enriches the flavor of the flowers. Like drying, curing is completed in a dark, cool storage area where the flowers can be regularly inspected and assessed.
In the beginning, the curing containers should be opened once or twice a day to let out the humidity and let in fresh air. After this initial period, the containers can be opened less frequently. At the end of curing, the flowers have an excellent odor and are at the peak of their flavor.
Extraction
The purpose of the extraction process is to separate cannabinoids, terpenes, and the other chemicals found in the cannabis plant. Though there are a variety of chemicals that can be garnered from the cannabis plant, the main goals of the many methods of extraction are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD).
-
CO₂
This method uses supercritical carbon dioxide under high pressure and controlled temperatures. It efficiently separates cannabinoids and terpenes without leaving harmful residues. It’s considered one of the cleanest and most precise extraction processes.
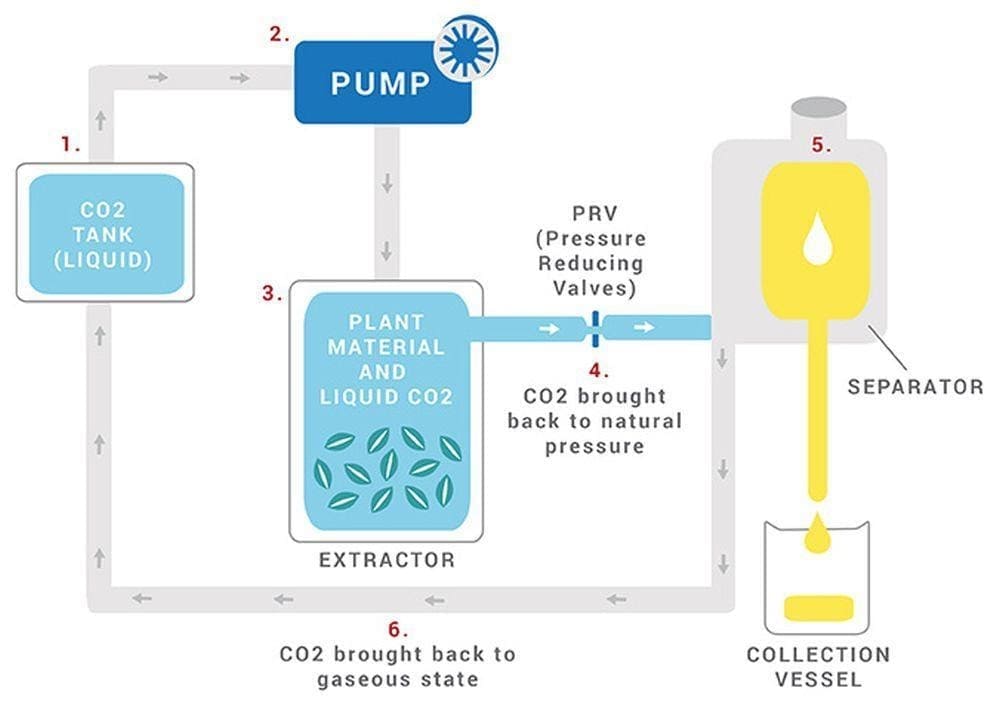
CO₂ Extraction Process (from manoxblog.com)
-
Alcohol
Ethanol or isopropyl alcohol is used to soak the cannabis flowers, breaking down trichomes and dissolving cannabinoids. After filtration and purging, the result is a cannabinoid-rich extract. This method is popular for producing full-spectrum CBD oils and Rick Simpson Oil (RSO).
-
Butane

Butane Extract (from analyticalcannabis.com)
Often used for creating Butane Hash Oil (BHO), this method involves pressurized butane or propane to strip cannabinoids from plant material. Once the solvent is vaporized and removed, a sticky concentrate remains. While effective, it must be done with specialized equipment due to flammability risks.
-
Mechanical
Mechanical methods separate trichomes without using solvents, relying instead on physical force. Though less efficient for large-scale production, these methods are valued for preserving plant integrity and avoiding chemical residues.

Cannabis Produced by Mechanical Extraction (from medium.com)
-
Ultrasound

Ultrasound Extractor and Agitator (from hielscher.com)
Ultrasound is used to create microscopic bubbles in the alcohol solvent. These bubbles burst against plant material, making it easier to release cannabinoids into the solvent. This enhances yield and reduces processing time.
-
Hydrodynamic
This cutting-edge technique uses frozen plant material, ultrasonication, and hydrocavitation to break open cell walls. It allows for whole-plant extraction—retaining a full spectrum of cannabinoids, terpenes, and nutrients. Molecules are then isolated, purified, and preserved through cold drying and distillation. Hydrodynamic extraction is notable for its ability to maintain high bioavailability, making it one of the most effective and nutrient-preserving options currently available.
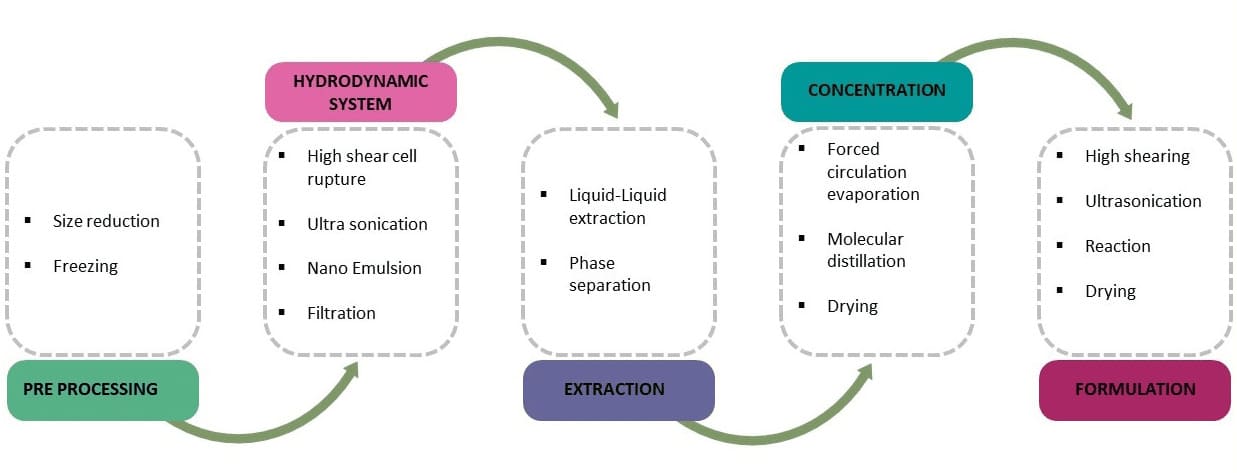
Steps to the Hydrodynamic Extraction Method (cleangreencannascience.com)
Chapter Three : Types of Cannabis Oil
The term cannabis oil is often used broadly, but it actually refers to a diverse range of oils derived wholly or partially from the cannabis plant. These can vary based on cannabinoid content, method of extraction, and intended use—ranging from hemp-derived CBD oil to high-potency THC concentrates. Each oil type has its own unique chemical profile, absorption rate, and therapeutic benefits. Understanding the differences is essential for choosing the right product.
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
THC oil is a psychoactive cannabis extract known for its euphoric and mind-altering effects. It’s primarily used for medical conditions such as epilepsy, chronic pain, and nausea. THC is one of over 140 cannabinoids found in cannabis, often concentrated at levels up to 35% in premium flowers. While THC remains a controlled substance in many areas, it has shown potential in treating seizure disorders, chemotherapy side effects, and neurological conditions.

Cannabidiol (CBD)

CBD oil is the most popular form of cannabis oil and is typically extracted from hemp flowers or CBD-rich cannabis strains. It contains little to no THC and is non-intoxicating, making it ideal for daily use.
Butane Hash or Butane Honey (BHO)
BHO is a potent resinous concentrate extracted using butane as the solvent. It comes in various consistencies like shatter, wax, and budder, depending on post-processing temperatures and humidity levels. Due to the volatile nature of butane, BHO production requires closed-loop systems for safety. While effective, it’s generally less favored for consumer use due to its flammable risk during extraction.
Rick Simpson Oil (RSO)

Rick Simpson Oil, or RSO, is a highly concentrated form of cannabis oil extracted using ethanol. It’s designed for medical use and is known for its high potency in both THC and CBD. RSO gained popularity for its potential role in treating skin cancer, though research remains ongoing. Its strength makes it a go-to option for patients with serious medical conditions.
Hemp Seed
Unlike CBD oil, hemp seed oil is pressed from the seeds of the hemp plant and contains little to no cannabinoids. It is rich in:
- Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids
- α-linolenic acid
- Vitamin E and essential minerals
Hemp

Hemp is an extremely rich source of CBD; its THC content is federally regulated. The oil can be full or broad spectrum, with the full spectrum version having all of the compounds from the hemp plant. Full spectrum hemp oil is the most potent form of hemp oil and contains the greatest concentration of health benefits. There is a belief that the total medical benefits of CBD can be found when all of the different elements are taken together as one instead of separately.
Chapter Four : Uses for Cannabis Oil
Although cannabis has gained recent attention in wellness and medical circles, its therapeutic use dates back thousands of years. From anti-inflammatory relief to neurological support, cannabis oil continues to be studied and used for a wide range of conditions. The three primary cannabis subspecies—Indica, Sativa, and Ruderalis—are cultivated for their distinct cannabinoid profiles, each offering unique medical applications.
Uses for Cannabis Oil
Digestive Health and Appetite Stimulation
Cannabis oil activates the body’s endocannabinoid receptors that regulate hunger. It boosts ghrelin production—the hormone responsible for appetite—which can be beneficial for those undergoing chemotherapy, suffering from anorexia, or needing to regain weight after illness.
Stress and Anxiety Relief
CBD has been shown to help regulate emotional responses by interacting with the brain’s amygdala and hippocampus—areas associated with fear and stress. It is commonly used to alleviate symptoms of:
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Panic attacks
- Social anxiety
Chronic Pain and Inflammation Control
Pain relief remains one of the most well-documented uses for cannabis oil. Both THC and CBD have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce:
- Fibromyalgia discomfort
- Arthritis inflammation
- Chemotherapy-related pain
- Neuropathic pain disorders
Eye Health: Glaucoma and Macular Degeneration
Cannabis oil can temporarily reduce intraocular pressure, which helps manage glaucoma symptoms and macular degeneration. However, relief is short-term, and it should not be relied on as a long-term cure.
Cancer Symptom Support
The use of cannabis for the treatment and prevention of cancer has been ongoing for many years. It is believed that cannabis oil can reduce the size of tumors and alleviate pain, weakness, nausea, and lack of appetite. There are several studies that paint cannabis as a treatment for pituitary, colon, lung, thyroid, prostate, breast, and brain cancers. A study completed in 2006 found that THC and CBD had a significant and lasting effect on breast cancer cells.
It is theorized that cannabis induces cancer cell death and cuts off the blood supply to cancerous tumors. Cannabis oil has also been found to be an alternative to chemotherapy, and it increases the vitality of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Skin Care and Dermatological Benefits
Every day, millions of skin cells die and need to be shed. Cannabis oil enhances this natural process and promotes the appearance of healthy skin. It produces lipids that treat dry skin, dandruff, and acne and is believed to fight free radical damage as well as reduce the stress linked to eczema, rosacea, and acne.
Cardiovascular Support
There are tentative studies that suggest that cannabis oil can be used to treat heart problems. According to the research, cannabis oil improves circulation and reduces blood pressure. At the present time, the data has not conclusively proven that cannabis oil can prevent heart attacks since only one study has been done on humans.
Relief for Sjogren’s Syndrome
Unfortunately, Sjogren‘s syndrome has no cure. Medical cannabis has been found to be a treatment that can alleviate the effects of some of the symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and inflammation. Cannabis oil is applied in a variety of ways, such as under the tongue or as a cream. It has been proven that cannabis oil significantly reduces inflammation and joint damage from the disease.
PTSD Management
CBD oil helps regulate neurotransmitters, improving mood stability, coping ability, and emotional regulation in individuals suffering from PTSD. Its interaction with dopamine receptors also promotes better sleep and reduced anxiety.
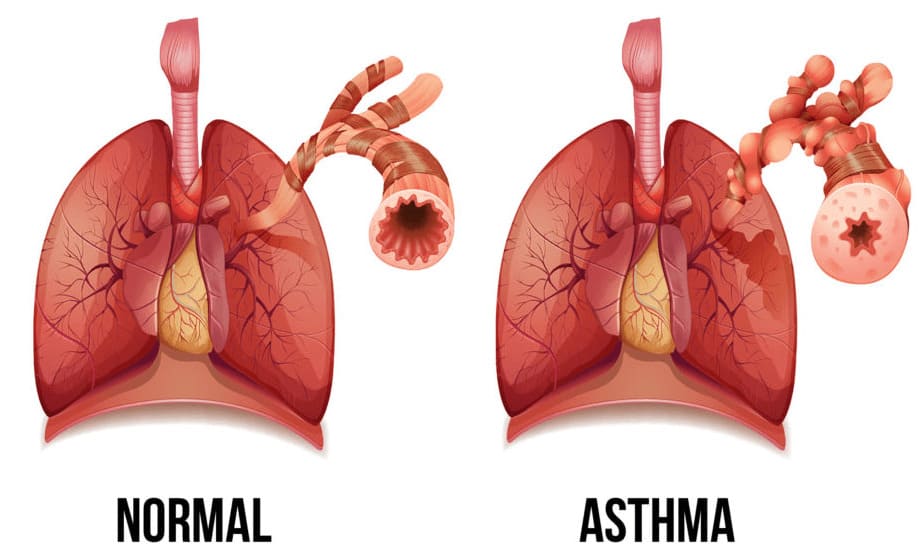
Asthma Symptom Relief
CBD’s anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic properties offer natural support for asthma sufferers. It helps reduce mucus production and modulates immune response by interacting with the endocannabinoid system—providing relief from airway constriction.
Sleep Aid and Insomnia Management
The calming effects of cannabis oil reduce restlessness and anxiety when trying to go to sleep, reduce sleep interruptions, and improve nighttime breathing. A major factor in sleep is the endocannabinoid system, which monitors sleep patterns as well as regulates and stabilizes sleep, and it is stimulated by CBD.
CBD has been found to be effective in addressing symptoms of sleep apnea (a disorder where patients stop breathing in their sleep) and insomnia by inducing states of physical and emotional calm. It stabilizes sleep patterns and alleviates sleep disorders.
Chapter Five : Finding the Right Cannabis Product
The first consideration when selecting the cannabis product to fit your situation is your goal. Cannabis oil can be used to improve sleep, as a health and wellness supplement, for stress relief, for muscle and joint pain, or general pain relief. As with all types of medications, it is important to know in advance your reason for taking CBD.
The next consideration is the strength that will be required to achieve your goals. CBD is measured in milligrams; this determines its potency and strength.
Finding the Right CBD Oil
There are three types of CBD oil. Knowing the differences between the types is essential to an understanding of CBD oil.
Types of CBD Oil
-
Full Spectrum
Includes all naturally occurring cannabinoids, terpenes, and trace amounts of THC. Known for the “entourage effect”, this whole-plant extract delivers the most comprehensive health benefits.
-
Broad Spectrum
Similar to full spectrum but without THC. Ideal for those who want multiple cannabinoids and terpenes without the psychoactive effects.
-
CBD Isolate
Contains pure cannabidiol only—no THC, terpenes, or other cannabinoids. A good choice for users who want high-dose CBD with no trace compounds.
CBD Strength
-
Low
Low strength CBD is for people who are new to the drug, have a fast metabolism, or have a low body mass index. The strength level of low strength CBD is 5 to 10 mg per dose.
-
Medium
Medium strength is for normal body types or for people who have had experience with CBD. Allowable dosages are between 15 to 30 mg.
-
High
People who are accustomed to the use of CBD, have a high body mass index, or have a high tolerance to CBD can use high strength CBD in dosages of 30 mg each.
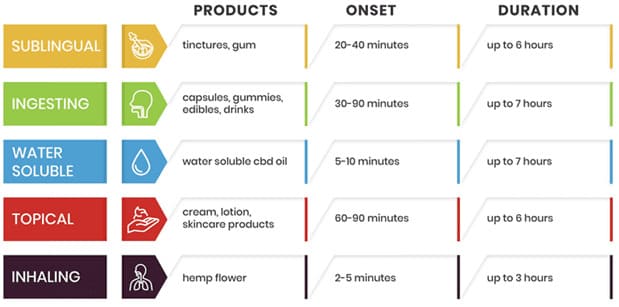
Methods of Application
Just like other wellness products, CBD oil can be taken in different forms depending on how quickly you want to feel results and how long the effects should last.
Sublingual
CBD tinctures and oils are dropped under the tongue and absorbed quickly. Effects are usually felt within 15–30 minutes.
Ingesting
CBD capsules, edibles, or drinks are easy to consume, but take longer to act—typically 30–90 minutes—due to digestion.
Water Soluble
Broken into nano-sized particles that are absorbed faster than traditional oils. Can be mixed into drinks for rapid effects (as quick as 15 minutes).
Topical
Lotions, creams, and balms are ideal for targeted relief—applied directly to the skin for muscle soreness, joint pain, or inflammation.
Inhalation
CBD vape pens and flower deliver fast-acting relief, often within minutes. However, inhalation may not be suitable for all users, especially those with respiratory concerns.
CBD can be taken regularly, such as in the morning and evening, or occasionally when symptoms or discomfort arises. There are various products that can conform to the different timing methods.
Another factor to consider when choosing a CBD oil is any dietary concerns such as allergies, having a vegan diet, and avoidance of gluten products. It is uncommon for gluten to be a factor in CBD processing, but certain contaminants can enter the product depending on the processing method.
Though uncommon, a small group of people are allergic to CBD; reactions can be caused by derivatives in the product or the CBD substances.
Chapter Six : Laws Regulating Cannabis Oil
The legal status of cannabis oil—particularly CBD and THC products—varies widely across the United States and continues to evolve. While federal regulations permit certain forms of hemp-derived CBD, individual states may impose stricter rules on production, distribution, and usage. Understanding these laws is critical for safe and compliant access.
Laws Regulating Cannabis Oil
When the push to legalize CBD began, CBD was classified as a Schedule 1 restricted substance due to its relationship to THC. The Farm Bill of 2014 laid out the distinction between cannabis and hemp, with marijuana having a higher amount of THC than hemp, which has a higher concentration of CBD.
The 2014 law allowed for the growth, transport, and research of hemp with a maximum THC level of 0.3%. THC remains a schedule 1 restricted substance and drug. This particular distinction has assisted in the research into the positive effects of CBD.
For greater clarification, the Farm Bill of 2018 specified that industrial hemp extracts are legal, permitting CBD oil to be used throughout the United States as long as it is extracted from industrial hemp. CBD extracted from marijuana can be used for medical purposes in compliance with individual state laws.
Forty six of the fifty states allow the use of CBD oil at differing levels. Some states allow it for therapeutic purposes, while others permit it for recreational and therapeutic purposes.
Included in the legal requirements are specifications and requirements for labeling, which must clearly identify the contents, such as THC or CBD or both and the percentages of each. Many of the restrictions are for the protection of children and require that packaging be child proof.
CBD product supplements require a supplement facts label on the back that includes an outline of secondary ingredients, warnings, and other instructions. Though it is not legislated, packaging of CBD should be in airtight green, blue, amber, or violet glass bottles since glass does not absorb oils and colored glass prevents deterioration from UV rays or artificial light.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) section 21 CFR 111.455 stipulates the packaging for food and dietary supplements but doesn‘t recognize CBD under the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA) of 1938. It does inspect CBD products being shipped across state lines for proper labeling.
Conclusion
Cannabis oil is a versatile product made from the flowers of hemp and marijuana plants. It can be rich in either CBD or THC, and is used for a wide variety of health, wellness, and medical purposes. To safely and legally access cannabis oil:
- Understand the type of product (CBD, THC, or full-spectrum)
- Verify its source and cannabinoid content
- The two main methods for removing and concentrating cannabinoids from cannabis are solvent based and mechanical.
- Follow all local laws and labeling requirements
- Choose the correct form and dosage based on your health goals
Whether you’re seeking stress relief, sleep support, or chronic pain management, choosing a properly extracted and legally compliant cannabis oil ensures the best results.